Women's Health: Understand Your Cycle and Take Control
Every month your body runs a short but intense program of hormones that decide whether you ovulate, bleed, or become pregnant. That sounds dramatic because it is — the menstrual cycle is a powerful sign of health. Knowing how it works helps you spot problems early and make smarter choices about contraception, fertility, and daily self-care.
How your cycle really works
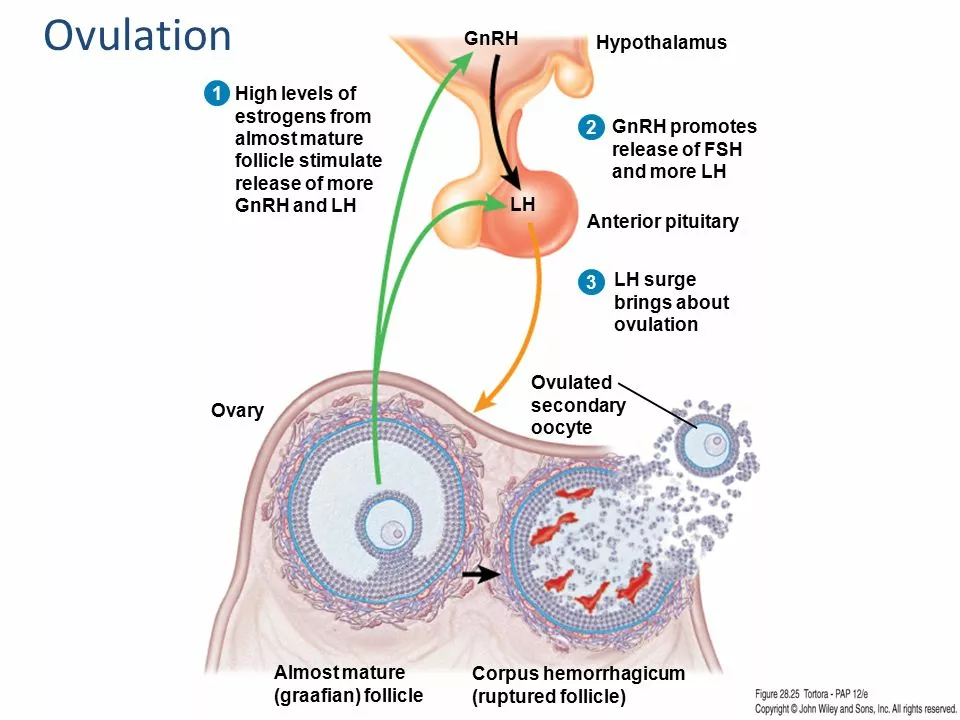
The cycle is driven by four main hormones: estrogen, progesterone, FSH, and LH. FSH tells eggs in the ovaries to start growing. A rise in estrogen thickens the uterine lining and triggers a spike in LH, which causes ovulation — the release of an egg. After ovulation, progesterone helps maintain the lining so a fertilized egg can implant. If pregnancy doesn't happen, hormone levels fall and bleeding begins.
Cycles vary. A common length is about 28 days, but 21–35 days can be normal for adults. Irregular periods, very heavy bleeding, or missed periods are signals worth checking. Conditions like PCOS, thyroid issues, or stress can change how those hormones behave.
Practical steps you can take today
Track your cycle. Use an app, a calendar, or a simple notebook. Note the first day of bleeding, how long it lasts, how heavy it is, pain level, mood changes, and any spotting. After 2–3 cycles you’ll see patterns that matter for birth control, planning pregnancy, or talking to a clinician.
Want to know when you ovulate? Try one or two easy tools: basal body temperature (BBT) taken each morning and ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) that detect the LH surge. BBT rises slightly after ovulation; OPKs give a clearer short-term signal. Combining both works well for many people.
If you have persistent symptoms — very heavy bleeding (soaks a pad/tampon in an hour), severe pain that stops you from daily life, sudden missed periods, or symptoms of high testosterone like rapid hair growth — schedule a visit with your GP or gynecologist. Ask for hormone tests or an ultrasound if needed. Early answers make treatment simpler.
Manage symptoms with targeted steps: for cramps try heat, regular gentle exercise, and over-the-counter pain relief; for heavy flow ask about tranexamic acid or hormonal options; for irregular cycles discuss birth-control pills or progestin therapies with your clinician. Supplements like iron can help if you’re anemic from heavy periods, but test before you start iron routinely.
Want to read more about the science behind ovulation and menstruation? Check our post 'The science behind the regulation of ovulation and menstruation' for a clear breakdown of how hormones interact and what can disrupt the cycle.
Use your cycle data. It helps with contraception choices, fertility planning, and spotting health issues early. If something feels off, trust that feeling and get checked — small shifts now can prevent bigger problems later.