NSAID Safety: What You Need to Know About Pain Relief and Risks
When you reach for ibuprofen, naproxen, or aspirin to ease a headache, sore muscles, or joint pain, you're using a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a class of medications that reduce inflammation and pain without steroids. Also known as NSAIDs, these drugs are among the most commonly used medicines worldwide—but their safety isn’t as simple as it seems. Millions rely on them daily, but many don’t realize how deeply they can affect the body beyond just stopping pain.
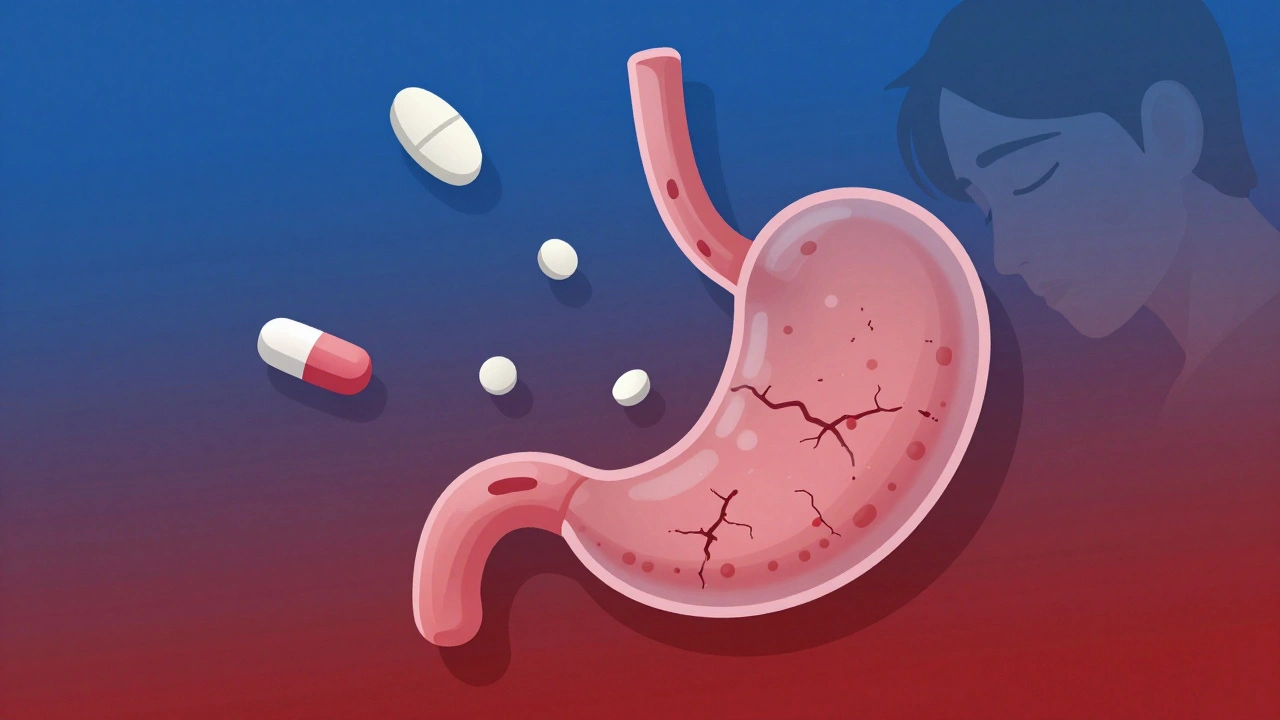
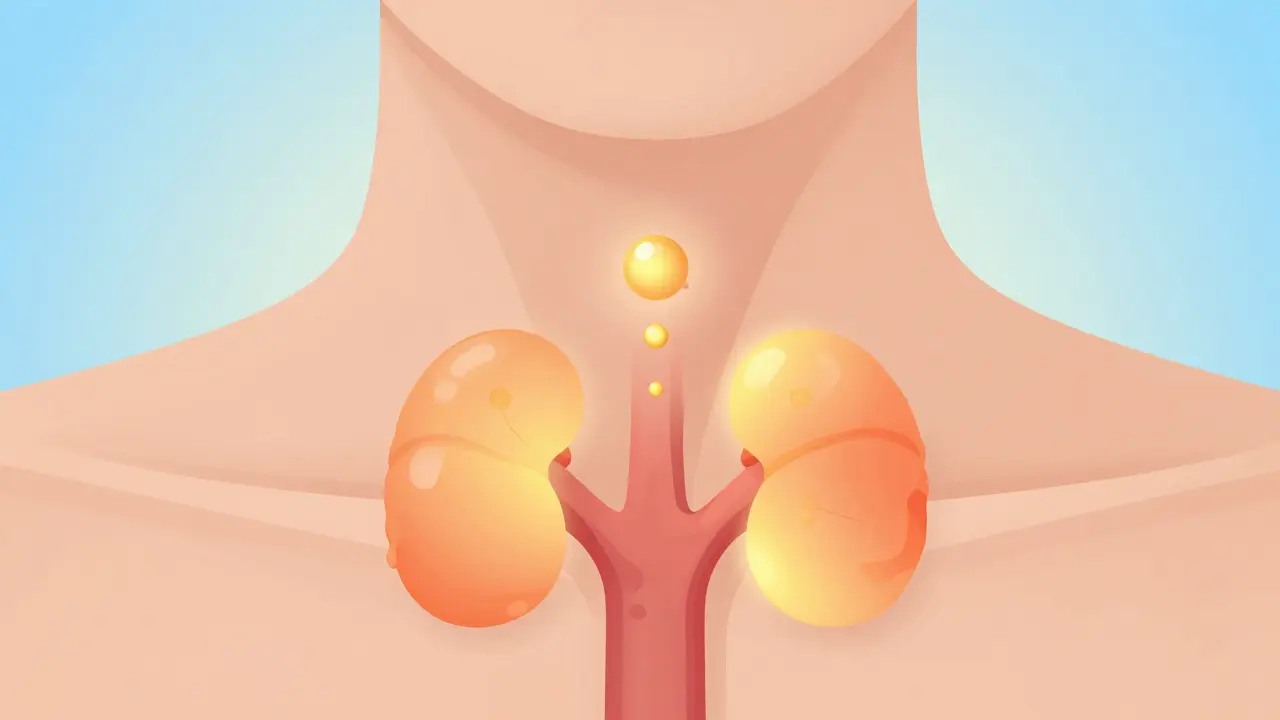
NSAID safety isn’t just about stomach upset. These drugs can quietly raise your risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney damage, and dangerous bleeding—especially if taken long-term or combined with other medications. For example, mixing NSAIDs with blood thinners or certain antidepressants can turn a routine pain reliever into a hidden threat. Even people who think they’re being careful—taking a pill only when needed—can be at risk if they’re also managing conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes. The FDA has issued strong warnings about NSAID use in people with heart disease, and studies show that long-term use increases the chance of gastrointestinal bleeding by up to four times, even in healthy adults.
What makes NSAID safety so tricky is how often these risks are overlooked. Many patients don’t connect their stomach pain, swelling in the ankles, or sudden fatigue to the pills they take for back pain. And doctors don’t always ask about OTC use. The truth is, NSAIDs aren’t harmless candy—they’re powerful chemicals that interfere with your body’s natural healing signals. If you’re using them regularly, you need to know what signs to watch for: black stools, unexplained weight gain, chest tightness, or sudden changes in urination. These aren’t normal side effects—they’re red flags.
Some people turn to NSAIDs because they’re avoiding stronger prescriptions, but that doesn’t make them safer. Others use them for chronic conditions like arthritis, thinking there’s no alternative. But there are options: physical therapy, targeted supplements like omega-3s, or even low-dose acetaminophen in some cases. The goal isn’t to scare you off NSAIDs—it’s to help you use them wisely. If you’re taking one regularly, talk to your pharmacist. Ask if your other meds interact. Check if your blood pressure has changed. See if your kidneys are being monitored. These aren’t just doctor’s notes—they’re your life-saving questions.
Below, you’ll find real stories and science-backed insights on how NSAIDs affect different people, what alternatives actually work, and how to spot danger before it’s too late. Whether you take them daily or just once in a while, this collection gives you the facts you won’t get from a bottle label.